2025 Checklist for Picking a Medical Assistant Program
Choosing a medical assistant program in 2025 is easier when you know what to verify before you enroll. This checklist breaks down accreditation, hands-on training, certification prep, scheduling, and support services so you can compare options clearly and avoid common surprises.
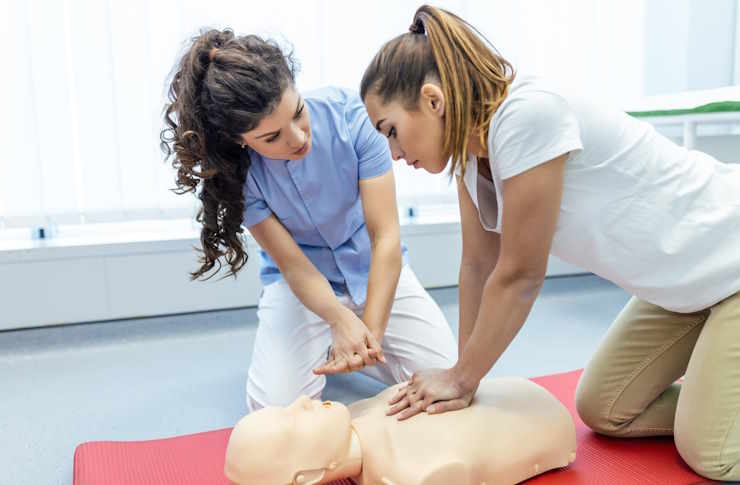
A smart program choice starts with clarity about what the role involves and what training must cover: patient intake, vital signs, clinical assistance, administrative workflows, and the privacy and safety standards that shape daily work in medical offices. In 2025, many schools also incorporate electronic health records practice and patient communication workflows, so it helps to compare curricula in detail rather than relying on program titles alone.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
2025 Career Guide: what should a program include?
A practical checklist begins with curriculum essentials. Look for coursework that clearly covers medical terminology, anatomy and physiology basics, pharmacology fundamentals, infection control, and administrative topics such as insurance basics and scheduling. Programs often describe these items differently, so ask for a course list and a sample weekly plan to see how much time is dedicated to clinical skills versus purely classroom instruction.
Also confirm how the program measures competency. Skills checkoffs, supervised lab practice, and structured assessments matter because they show whether you will repeatedly perform core tasks (like taking vitals or preparing exam rooms) under observation. If you are using a “2025 Career Guide” approach to comparing schools, prioritize programs that publish learning outcomes and explain how students are evaluated in labs and during any clinical placement.
How to find the right medical assistant training program for you
Fit is not only about location; it is about how training is delivered and supported. Start by identifying constraints: your work hours, commute tolerance, caregiver responsibilities, and preferred learning style. Then match those to the program format. Some schools offer campus-based labs with online theory modules, while others are largely in-person. For any online or hybrid option, ask how hands-on skills are taught and assessed, since clinical competencies still require supervised practice.
Next, evaluate student support. Ask whether the program provides tutoring, study skills help, and structured coaching for clinical professionalism (communication, punctuality, documentation habits). If English is not your first language or you are returning to school after time away, these supports can have a real impact on completion. A strong checklist item is transparency: programs should clearly describe attendance policies, remediation options, and how quickly instructors provide feedback.
2025 Career Guide: how to compare credentials, accreditation, and externships
Credential type affects timeline and depth. Medical assistant education is commonly offered as a certificate/diploma or an associate degree. Certificates may be shorter and focused, while associate programs typically include general education courses alongside core medical assisting content. Neither option guarantees employment outcomes, so decide based on your learning goals, time horizon, and budget.
Accreditation and approval language can be confusing, so verify it carefully. In the U.S., reputable medical assisting programmatic accreditors include CAAHEP (Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs) and ABHES (Accrediting Bureau of Health Education Schools). Institutional accreditation (for the school as a whole) is separate from programmatic accreditation (for the medical assisting program). Ask which applies and request the program’s status and accrediting body in writing.
Externship or practicum requirements are another key differentiator. A checklist item for 2025 is to confirm the placement process: Does the school arrange sites, or is the student expected to find one? How many hours are required, and in what settings (family practice, urgent care, pediatrics, specialty clinics)? Ask how supervision is handled, what tasks students are allowed to perform, and how performance is evaluated. These details affect how prepared you feel at graduation.
Certification preparation is worth mapping early. Common national certifications include CMA (AAMA), RMA (AMT), and options from NHA (such as CCMA). Eligibility rules vary by credential and may depend on graduating from an accredited program or meeting other criteria. If your goal is certification, ask which exam the curriculum aligns to, whether prep is integrated into courses, and what recent graduates typically do to get ready (practice tests, review sessions, or dedicated prep modules). If you are searching “How to Find the Right Medical Assistant Training Program for You,” include exam eligibility and prep support as non-negotiable comparison points.
Finally, read policies that affect real life: immunization and background check requirements, drug screening, CPR training expectations, and technology needs (for example, access to a reliable computer for online components). These are common in healthcare training and can influence both cost and timeline.
A complete 2025 checklist should leave you with a short list of programs that are transparent about outcomes, clear about accreditation and clinical hours, and realistic about the time and structure needed to build competence.




