Collaborative Tools for Architects and Contractors
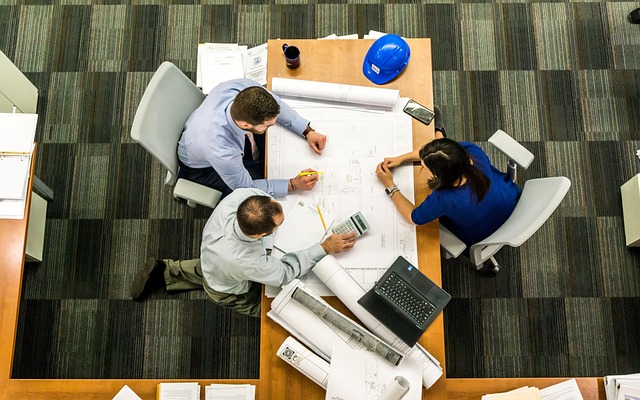
Modern construction projects demand seamless coordination between architects, contractors, and project teams. Collaborative software tools have transformed how professionals communicate, share designs, and manage workflows throughout the building process. These digital platforms enable real-time updates, reduce errors, and streamline project timelines. Understanding the available technology options helps construction professionals select solutions that enhance productivity and foster better teamwork across all project phases.
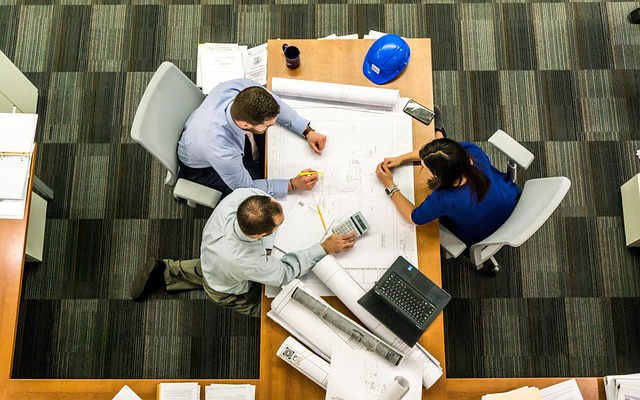

The construction industry has embraced digital transformation through specialized software that connects design teams with field personnel. These platforms address common challenges such as version control, communication gaps, and document management. By centralizing project information, collaborative tools reduce costly mistakes and keep everyone aligned on project goals and timelines.
Thinking About Construction Software?
Construction software encompasses a wide range of applications designed to improve project outcomes. When evaluating options, professionals should consider their specific workflow needs, team size, and project complexity. Cloud-based platforms offer accessibility from any location, enabling remote collaboration and mobile access on job sites. Key features to assess include document sharing capabilities, markup tools, real-time notifications, and integration with existing systems. Many solutions offer modular approaches, allowing teams to adopt features gradually rather than overhauling entire workflows at once. Security considerations are paramount, as construction documents often contain sensitive client information and proprietary designs. Look for platforms with robust encryption, user permission controls, and reliable backup systems.
How Construction Planning Software Works
Construction planning software operates by creating a digital ecosystem where project stakeholders can access current information simultaneously. These systems typically begin with project setup, where administrators establish user roles, permissions, and folder structures. Document management forms the core functionality, allowing teams to upload drawings, specifications, contracts, and schedules to a centralized repository. Version control automatically tracks changes, maintaining a complete history of revisions and eliminating confusion about which documents are current. Communication features include threaded discussions, request for information workflows, and automated notifications that alert relevant parties when action is required. Many platforms incorporate task management and scheduling tools that link activities to responsible parties with defined deadlines. Integration capabilities allow data exchange with accounting software, design applications, and field management tools. Mobile applications extend functionality to job sites, enabling field teams to access plans, submit daily reports, capture photos, and log issues without returning to the office. Analytics dashboards provide project visibility through metrics tracking budget status, schedule adherence, and outstanding issues.
Ways to Use BIM Software Tools
Building Information Modeling represents a significant advancement in construction collaboration technology. BIM software creates intelligent 3D models containing detailed information about every building component, from structural elements to mechanical systems. Architects use BIM tools to develop designs that automatically generate construction documentation, ensuring consistency between drawings and specifications. Contractors leverage BIM models for clash detection, identifying conflicts between different building systems before construction begins, which prevents costly field changes. Quantity takeoffs become more accurate as BIM software calculates material requirements directly from model elements, improving cost estimation and procurement planning. Construction sequencing, known as 4D BIM, adds time dimensions to models, allowing teams to visualize building phases and optimize construction logistics. Facility managers benefit from BIM by receiving as-built models containing maintenance information, equipment specifications, and warranty details for long-term building operations. Coordination meetings become more productive when teams review 3D models together, making it easier to visualize complex assemblies and resolve design questions. Cloud-based BIM collaboration platforms enable multiple disciplines to work on shared models simultaneously, with changes synchronized across all users in real time.
| Software Type | Provider Examples | Key Features | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Project Management | Procore, Autodesk Construction Cloud | Document control, RFIs, submittals | $300-$800 per user/year |
| BIM Collaboration | Autodesk BIM 360, Trimble Connect | Model coordination, clash detection | $500-$1,200 per user/year |
| Field Management | PlanGrid, Fieldwire | Mobile access, punch lists, daily reports | $200-$500 per user/year |
| Scheduling | Primavera P6, Microsoft Project | CPM scheduling, resource allocation | $400-$2,000 per user/year |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Selecting the Right Platform for Your Team
Choosing appropriate collaborative tools requires careful assessment of project requirements and team capabilities. Small firms may benefit from user-friendly platforms with straightforward interfaces and lower learning curves, while large enterprises might need comprehensive solutions with advanced customization options. Trial periods allow teams to test functionality with actual project data before committing to subscriptions. Training resources and customer support quality significantly impact successful adoption, as even powerful software provides little value if team members cannot use it effectively. Scalability matters for growing firms, ensuring chosen platforms can accommodate expanding user bases and increasingly complex projects. Consider interoperability with partner organizations, as many projects involve external consultants and subcontractors who may use different primary systems. Total cost of ownership extends beyond subscription fees to include implementation time, training expenses, and potential productivity dips during transition periods.
Implementation Best Practices
Successful software adoption requires thoughtful planning and change management. Begin with pilot projects that allow teams to learn new systems on less critical work before rolling out company-wide. Designate internal champions who receive advanced training and provide peer support during transition periods. Establish clear protocols for file naming, folder organization, and communication workflows to prevent digital chaos. Regular check-ins during initial months help identify issues early and reinforce proper usage patterns. Measure success through defined metrics such as RFI response times, document retrieval speed, or reduction in rework incidents. Continuous improvement involves gathering user feedback and adjusting workflows as teams become more proficient with available tools.
Collaborative technology continues evolving, with emerging capabilities like artificial intelligence for document review, augmented reality for field visualization, and advanced analytics for predictive project insights. Construction professionals who embrace these tools position themselves for greater efficiency, reduced risk, and improved project outcomes in an increasingly competitive industry.