Digital Platform Payment Flexibility for Smartphones
Smartphone purchases have evolved beyond traditional financing, with digital platforms now offering flexible payment solutions that spread costs over time. These programs allow consumers to acquire the latest devices without immediate full payment, making technology more accessible. Understanding how these arrangements work, their operational structure, and practical considerations helps consumers make informed decisions about device purchases.
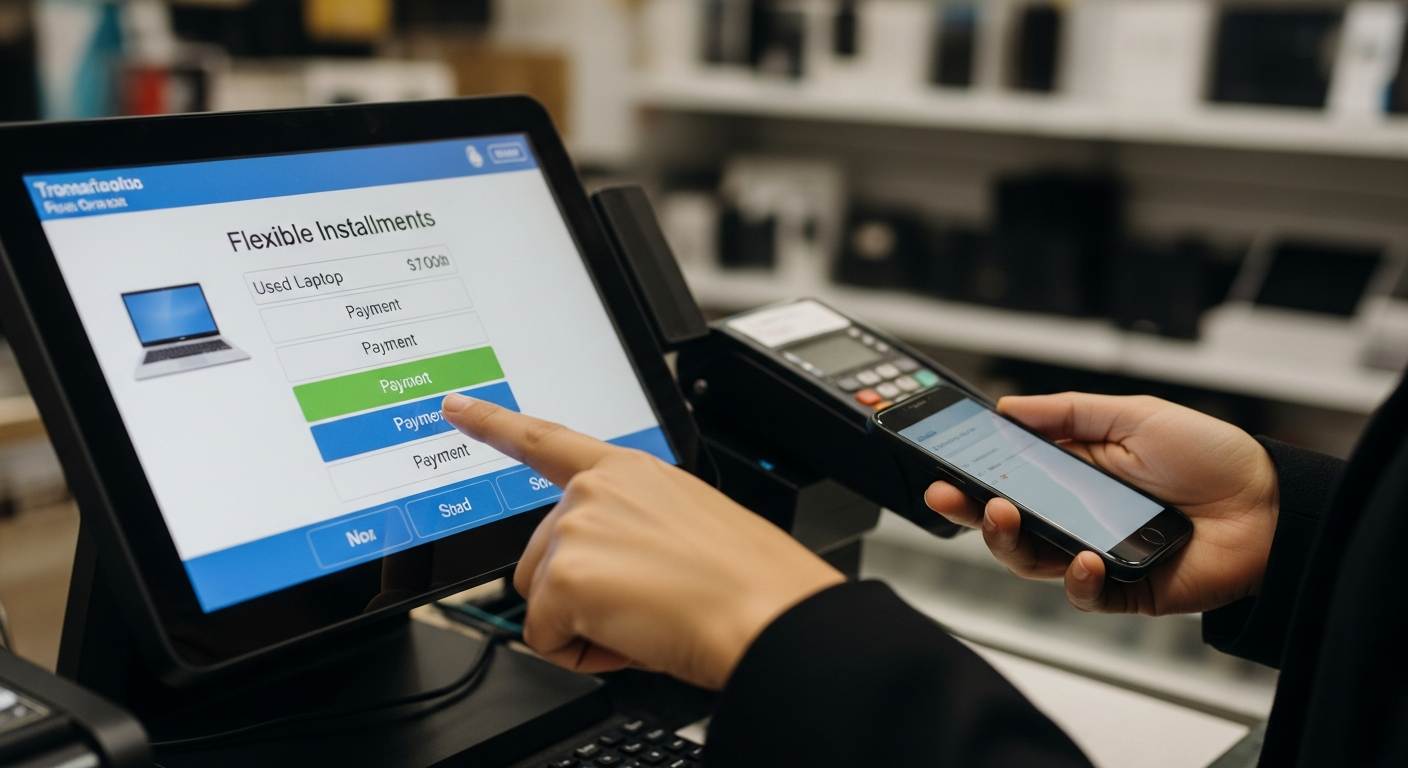

Modern smartphone acquisition has transformed through digital payment flexibility programs that enable consumers to obtain devices through installment arrangements. These solutions bridge the gap between immediate device needs and budget constraints, offering structured payment plans managed through various digital platforms and retail channels.
How Buy Now Pay Later Phone Programs Are Structured Across Digital Platforms
Digital payment flexibility programs for smartphones typically divide the total device cost into equal installments over predetermined periods, commonly ranging from 3 to 24 months. Platforms integrate these programs directly into checkout processes, conducting instant approval assessments based on consumer creditworthiness. The structure generally includes zero or low interest rates for shorter terms, with longer periods potentially carrying interest charges. Major digital platforms partner with financial service providers to underwrite these arrangements, creating seamless integration between device selection and payment approval. Some programs require initial down payments while others offer full deferral, depending on the device value and consumer credit profile. Automated payment systems link to debit cards, credit cards, or bank accounts, with scheduled withdrawals occurring on specified dates throughout the agreement period.
How Companies Manage Buy Now Pay Later Phone Offerings in Operations
Companies operating these programs maintain sophisticated backend systems that handle risk assessment, payment processing, and account management. Operational workflows begin with real-time credit evaluations using proprietary algorithms that analyze multiple data points beyond traditional credit scores. Approval decisions typically occur within seconds, enabling immediate transaction completion. Companies manage inventory allocation separately for these programs, ensuring device availability matches approved financing capacity. Customer service operations address payment modifications, early payoff options, and default management through dedicated support channels. Financial reconciliation occurs between platform operators, device manufacturers, and financial institutions, with each party receiving their portion of the transaction value according to partnership agreements. Companies monitor program performance through metrics including approval rates, default percentages, and customer lifetime value, adjusting eligibility criteria and terms based on portfolio performance.
What Working With Buy Now Pay Later Phone Services Involves in Practice
Consumers engaging with these services navigate a straightforward application process during device checkout. The experience begins with selecting the payment flexibility option, followed by providing personal and financial information for assessment. Approved users review terms including payment amounts, schedule, and any applicable fees before finalizing purchases. Practical management involves ensuring sufficient funds for scheduled payments, as missed payments may incur fees and affect credit standing. Many platforms provide account dashboards showing remaining balance, upcoming payments, and early payoff options. Device ownership typically transfers immediately upon purchase, unlike traditional leasing arrangements, meaning consumers can modify, sell, or trade devices subject to remaining payment obligations. Some programs include device protection plans or upgrade options after completing specified payment milestones.
| Service Provider | Typical Term Options | Cost Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Affirm | 3, 6, 12, 24 months | 0-30% APR depending on term and creditworthiness |
| Klarna | 4 installments, 6-36 months | Interest-free for 4 payments, variable rates for longer terms |
| Afterpay | 4 bi-weekly payments | Interest-free, late fees apply for missed payments |
| PayPal Pay in 4 | 4 bi-weekly payments | Interest-free, no fees if paid on time |
| Apple Card Monthly Installments | 12, 24 months | 0% APR for Apple products |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Program Eligibility and Approval Considerations
Eligibility requirements vary across platforms but generally include minimum age requirements of 18 years, valid identification, and verifiable income or banking history. Credit assessments differ from traditional financing, with some providers focusing on banking activity and payment history rather than credit scores alone. Approval amounts depend on individual financial profiles, potentially limiting device selection for first-time users. Building positive payment history with these services can increase future approval amounts and improve terms. Some platforms report payment activity to credit bureaus, potentially affecting credit scores positively with consistent payments or negatively with defaults. Understanding specific provider policies regarding credit reporting helps consumers anticipate impacts on broader financial profiles.
Comparing Traditional Carrier Financing and Digital Payment Flexibility
Traditional carrier financing through mobile service providers differs from digital payment flexibility programs in several aspects. Carrier programs typically require service contracts linking device payments to monthly service bills, while digital platforms separate device financing from service selection. Carrier financing often includes upgrade programs allowing early device replacement, whereas digital platforms focus solely on purchase completion. Interest rates and fees may vary, with carriers sometimes subsidizing device costs through service revenue. Digital platforms offer flexibility to purchase unlocked devices compatible with any carrier, providing greater service provider choice. Understanding these distinctions helps consumers select arrangements aligning with their service preferences and financial situations.
Financial Planning and Responsible Usage
Successful engagement with payment flexibility programs requires careful financial planning and budget management. Consumers should assess total monthly obligations including device payments alongside other financial commitments before approval. Creating payment reminders and maintaining adequate account balances prevents missed payments and associated fees. Reviewing terms for early payoff options allows accelerated debt elimination when financial circumstances improve. Avoiding simultaneous multiple payment plans prevents overextension and maintains manageable debt levels. Understanding the total cost including any interest charges enables comparison with alternative purchase methods such as saving for outright purchase or using existing credit facilities. Responsible usage of these programs provides device access while maintaining financial stability and credit health.
Conclusion
Digital payment flexibility programs have democratized smartphone access by removing immediate payment barriers while introducing structured financial obligations. These programs operate through sophisticated digital platforms managing approval, payment processing, and account maintenance with minimal consumer friction. Practical engagement requires understanding program structure, maintaining payment discipline, and recognizing how these arrangements fit within broader financial management. As these services continue evolving, they represent significant shifts in consumer technology acquisition, balancing immediate access with manageable financial commitment.