Technology Control Systems for Distributed Teams
Distributed teams rely on technology control systems to maintain security, productivity, and seamless operations across multiple locations. As remote work becomes standard practice, organizations need robust solutions to manage devices, applications, and data access from a central platform. These systems enable IT administrators to monitor, configure, and secure endpoints regardless of where employees work, ensuring consistent policies and rapid response to potential threats while supporting workforce flexibility.
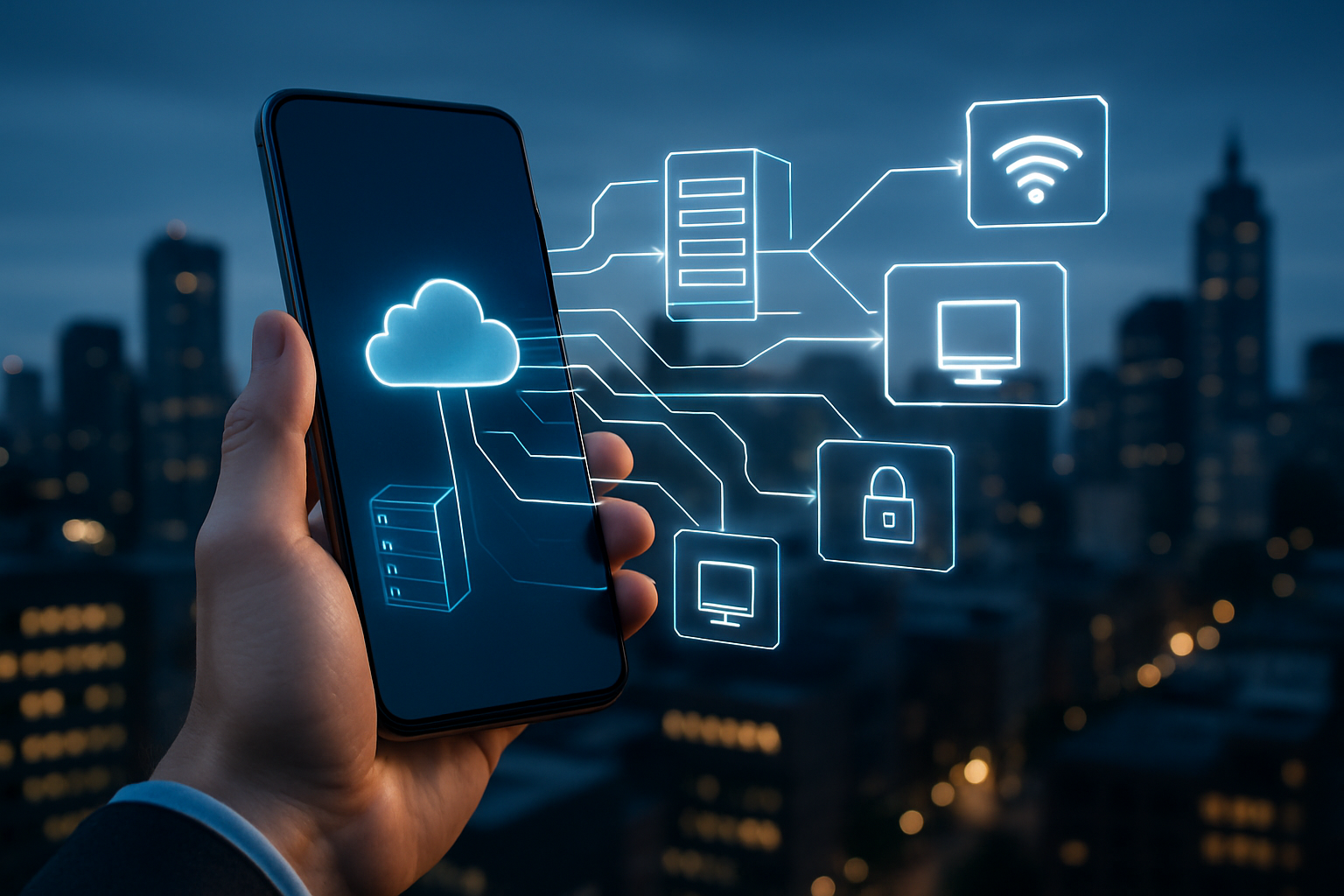

Modern organizations face unprecedented challenges in managing technology infrastructure across geographically dispersed workforces. Technology control systems provide the framework necessary to maintain operational efficiency, security compliance, and device standardization when teams operate from various locations. These platforms have evolved from simple monitoring tools into comprehensive management solutions that address the complex needs of contemporary distributed work environments.
The shift toward remote and hybrid work models has accelerated the adoption of centralized control systems. Companies must now oversee laptops, smartphones, tablets, and other endpoints without physical access to devices. This reality demands sophisticated software capable of delivering real-time visibility, automated policy enforcement, and streamlined troubleshooting across diverse operating systems and device types.
Mobile Device Management
Mobile device management represents a critical component of technology control systems, focusing specifically on smartphones and tablets used by distributed team members. These solutions allow administrators to configure security settings, deploy applications, enforce password policies, and remotely wipe data if devices are lost or stolen. Organizations can establish separate profiles for personal and work data, maintaining privacy while protecting corporate information.
MDM platforms typically support iOS, Android, and other mobile operating systems through unified consoles. Administrators can push configuration updates, monitor compliance status, and generate reports on device usage patterns. Integration with identity management systems enables conditional access policies that restrict sensitive data based on device health, location, or authentication strength. This layered approach helps organizations balance security requirements with user convenience.
Remotely Manage Mobile Devices
Remote management capabilities extend beyond initial configuration to ongoing maintenance and support throughout device lifecycles. IT teams can troubleshoot issues, install patches, and update applications without requiring physical possession of devices. This functionality reduces downtime and eliminates the logistical challenges associated with collecting devices from remote workers.
Modern platforms offer over-the-air enrollment processes that simplify device onboarding for new employees. Users receive automated instructions to register their devices, after which management profiles are installed automatically. Administrators can then deploy required applications, certificates, and network settings remotely. When employees leave the organization, devices can be unenrolled and corporate data removed without affecting personal information on employee-owned devices.
Get Insights on Remote Device Management
Data-driven insights transform device management from reactive troubleshooting to proactive optimization. Technology control systems collect telemetry on device performance, application usage, security incidents, and compliance status. Analytics dashboards present this information in actionable formats, highlighting trends and anomalies that require attention.
Organizations can identify devices with outdated operating systems, track application adoption rates, and measure the effectiveness of security policies. These insights inform decisions about hardware refresh cycles, software licensing, and security investments. Predictive analytics can flag devices likely to experience failures, enabling preventive maintenance before problems impact productivity. Comprehensive reporting capabilities also support compliance audits by documenting security controls and policy enforcement.
| Solution Category | Provider Examples | Key Features | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enterprise MDM Platforms | Microsoft Intune, VMware Workspace ONE | Full device lifecycle management, application deployment, conditional access | $6-$15 per device/month |
| Unified Endpoint Management | Jamf Pro, IBM MaaS360 | Cross-platform support, automated workflows, threat detection | $8-$20 per device/month |
| Cloud-Based Management | Google Workspace, Cisco Meraki | Browser-based administration, zero-touch enrollment, integration with productivity suites | $5-$12 per device/month |
| Open Source Solutions | ManageEngine, Miradore | Customizable frameworks, community support, basic management functions | Free to $4 per device/month |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Implementation Considerations for Distributed Teams
Successful deployment of technology control systems requires careful planning and stakeholder engagement. Organizations must balance security requirements with user experience, avoiding overly restrictive policies that frustrate employees and reduce productivity. Clear communication about monitoring capabilities and data privacy helps build trust and ensures compliance with legal requirements.
Integration with existing IT infrastructure is essential for seamless operations. Control systems should connect with identity providers, security information and event management platforms, help desk software, and asset management databases. This integration eliminates data silos and enables automated workflows that reduce administrative overhead. Pilot programs allow organizations to test configurations and gather feedback before full-scale rollout.
Security and Compliance Benefits
Technology control systems strengthen security postures by enforcing consistent policies across all managed devices. Encryption requirements, screen lock timeouts, and application whitelisting reduce attack surfaces and limit potential damage from compromised devices. Real-time threat detection identifies suspicious behavior and triggers automated responses such as network isolation or forced password resets.
Compliance frameworks often mandate specific controls for devices accessing regulated data. Healthcare organizations must meet HIPAA requirements, while financial institutions face regulations from multiple agencies. Control systems provide the documentation and technical controls necessary to demonstrate compliance during audits. Geofencing capabilities can restrict data access based on device location, preventing unauthorized access from high-risk regions.
Future Trends in Device Management
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming technology control systems from rule-based platforms to adaptive solutions that learn from user behavior. Predictive models identify security risks before they materialize, while intelligent automation handles routine tasks without human intervention. Zero-trust architectures are becoming standard, treating every access request as potentially malicious regardless of source.
The proliferation of Internet of Things devices in workplace settings expands the scope of technology control systems beyond traditional computers and phones. Organizations must manage smart displays, wearables, sensors, and specialized equipment through unified platforms. Edge computing capabilities enable local processing and decision-making, reducing latency and bandwidth requirements for distributed deployments.
Technology control systems have become indispensable for organizations supporting distributed teams. These platforms provide the visibility, control, and automation necessary to maintain security and productivity across diverse device fleets. As work continues evolving beyond traditional office boundaries, investment in robust management solutions will remain a strategic priority for forward-thinking organizations.