Warehouse Organization for Diverse Item Management
Managing diverse inventory in warehouse environments requires strategic planning and systematic approaches to ensure efficiency. From electronics to textiles, pharmaceutical products to automotive parts, each item category presents unique storage challenges and handling requirements. Effective warehouse organization maximizes space utilization, reduces retrieval times, and minimizes product damage while maintaining accurate inventory tracking across multiple product lines.
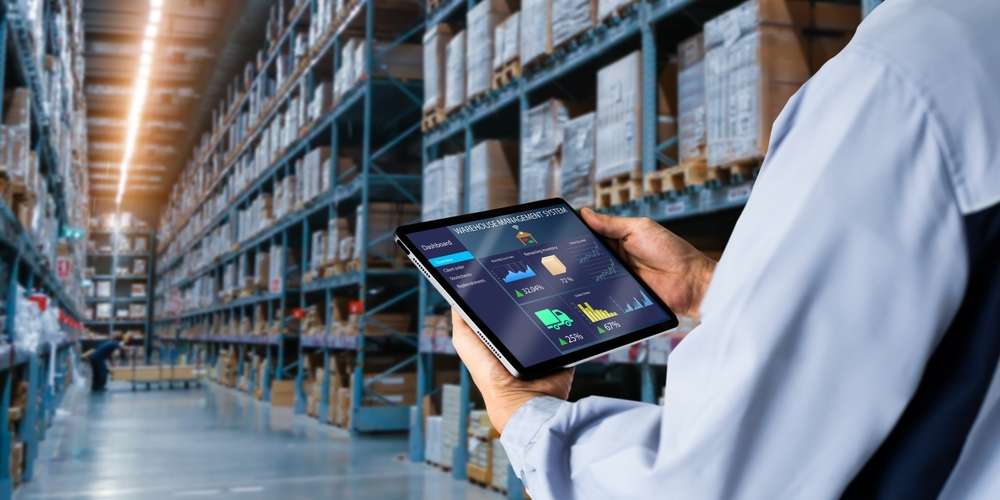

Understanding Warehouse Inventory Categories
Warehouse inventory encompasses numerous product types, each requiring specific handling protocols and storage conditions. Electronics demand climate-controlled environments to prevent moisture damage, while hazardous materials need specialized containment systems. Perishable goods require temperature monitoring, and fragile items need protective packaging solutions. Understanding these diverse requirements forms the foundation of effective warehouse organization.
Storage Systems for Different Product Types
Implementing appropriate storage systems depends heavily on product characteristics and turnover rates. High-density pallet racking suits bulk items with consistent dimensions, while bin storage systems work effectively for smaller components. Cantilever racks accommodate long items like pipes or lumber, whereas drive-in racking maximizes space for homogeneous products. Automated storage and retrieval systems enhance efficiency for high-volume operations with diverse inventory types.
Inventory Classification Methods
ABC analysis categorizes inventory based on value and turnover frequency, helping prioritize storage locations and handling procedures. A-items represent high-value products requiring prime locations and frequent monitoring. B-items occupy intermediate zones with moderate access requirements. C-items, typically low-value but numerous, can be stored in less accessible areas. This classification system optimizes warehouse layout and resource allocation across diverse product ranges.
Technology Integration in Modern Warehouses
Warehouse management systems streamline inventory tracking across multiple product categories through barcode scanning and RFID technology. Real-time inventory updates prevent stockouts and overstock situations while providing accurate location data for diverse items. Integration with enterprise resource planning systems enables seamless coordination between procurement, storage, and distribution activities. Mobile devices and handheld scanners facilitate efficient picking and put-away processes for varied inventory types.
Safety Protocols for Mixed Inventory
Diverse inventory requires comprehensive safety protocols addressing specific hazards associated with different product types. Chemical storage demands proper ventilation and spill containment measures, while heavy machinery parts require secure mounting and lifting equipment. Staff training programs must cover handling procedures for each product category, including personal protective equipment requirements and emergency response protocols. Regular safety audits ensure compliance with industry regulations and minimize workplace incidents.
Cost Considerations for Warehouse Organization
Implementing effective warehouse organization systems involves various cost factors that businesses must consider. Initial setup expenses include storage equipment, technology systems, and facility modifications. Ongoing operational costs encompass staff training, maintenance, and system upgrades.
| Component | Typical Cost Range | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Pallet Racking System | £50-150 per position | Height, load capacity, accessibility |
| Warehouse Management Software | £5,000-50,000 annually | Features, user count, integration needs |
| Barcode Scanning Equipment | £100-500 per device | Scanning range, durability, connectivity |
| Staff Training Programs | £200-800 per employee | Complexity, duration, certification requirements |
| Climate Control Systems | £10,000-100,000+ | Warehouse size, temperature requirements |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Optimizing Warehouse Layout Design
Effective warehouse layout design considers product flow patterns, storage requirements, and operational efficiency. Zone-based organization groups similar products while maintaining logical picking sequences. Wide aisles accommodate material handling equipment, while narrow aisles maximize storage density for slower-moving items. Cross-docking areas facilitate direct transfer of fast-moving products, reducing handling time and storage costs. Strategic placement of receiving and shipping areas minimizes internal transportation distances.
Successful warehouse organization for diverse item management requires balancing multiple factors including product characteristics, operational efficiency, safety requirements, and cost considerations. Regular evaluation and adjustment of organizational systems ensure continued effectiveness as inventory mix and business requirements evolve. Implementing systematic approaches to storage, classification, and technology integration creates a foundation for scalable warehouse operations capable of handling increasingly diverse product portfolios.